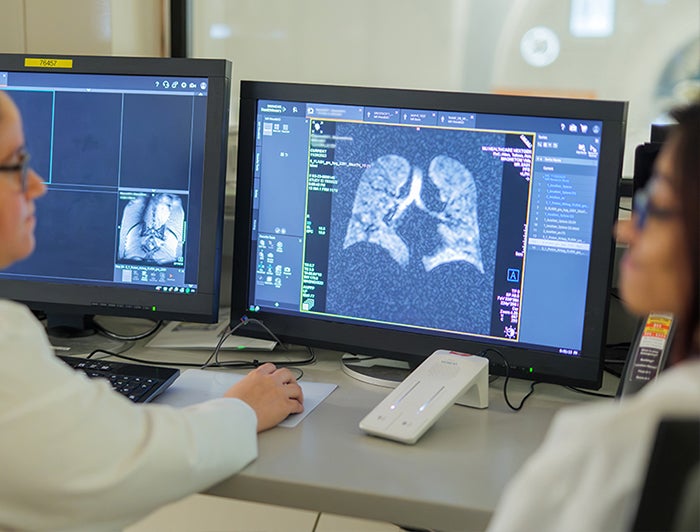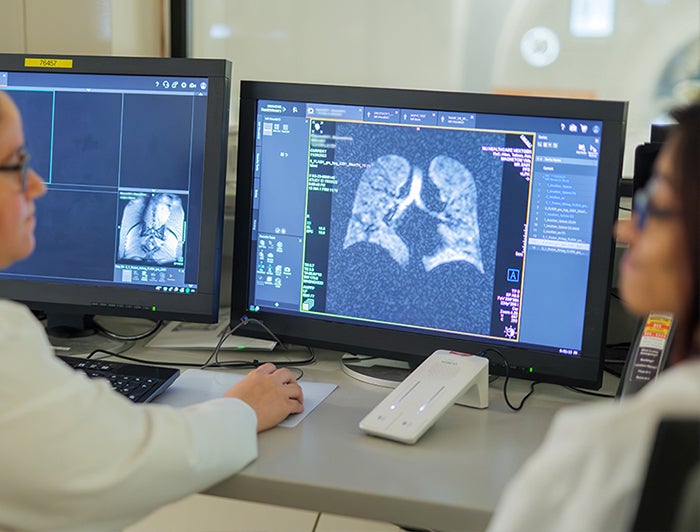
MU Health Care is the second hospital in the United States to perform lung scans using xenon MRI. Xenon MRI is a breakthrough technology that promises to significantly improve the ability of healthcare providers to evaluate lung diseases such as cystic fibrosis, asthma, COPD, and cancer.
Xenon MRI is similar to traditional MRI diagnostics in that magnets are used to align the body's atoms during the scan. However, traditional MRI looks for hydrogen atoms in water in body tissues, making it less effective at fully imaging the air-filled lungs. Xenon MRI overcomes this hurdle by utilizing hyperpolarized xenon gas, a non-reactive substance that is inhaled by the patient and held in the lungs for 10 to 15 seconds during the scan.
The result is a more complete picture of the lungs and their function. Clinicians receive detailed 3D images of ventilated lung airspaces. This test can also be used to quantify detailed aspects of lung function, such as lung microstructure and gas exchange.
MU Healthcare physicians say this more complete picture is a game-changer in the treatment of lung diseases. In the past, treatment strategies began like a puzzle, with doctors and patients working from end to end to build a complete picture and determine a path to diagnosis and treatment. But before xenon MRI, the images often had gaps, sometimes significant gaps.
“For one patient, this may be one piece of the puzzle; for another patient, this may be half the puzzle,” said pulmonologist Dr. Zach Holliday. I am. [xenon MRI] It might really shed some light on the puzzle we were missing pieces of, and now we can finally complete it. ”
The adoption of this new testing tool is part of MU Healthcare's NextGen Precision Health initiative, which brings together innovators from the University of Missouri and three other research universities in the UM System to make life-changing advances in precision health. I aim to pursue it.
learn more