Dr. Raymond Lee, a dentist at Pacific Dental and Orthodontic Care in Hong Kong, emphasizes that good oral care is not just about supporting the health of your teeth and gums.
“It affects the health of our entire body,” he says. how? The mouth is connected to important systems such as the respiratory, digestive and cardiovascular systems and is home to a large number of bacteria and microorganisms, some of which can be harmful to our health. .
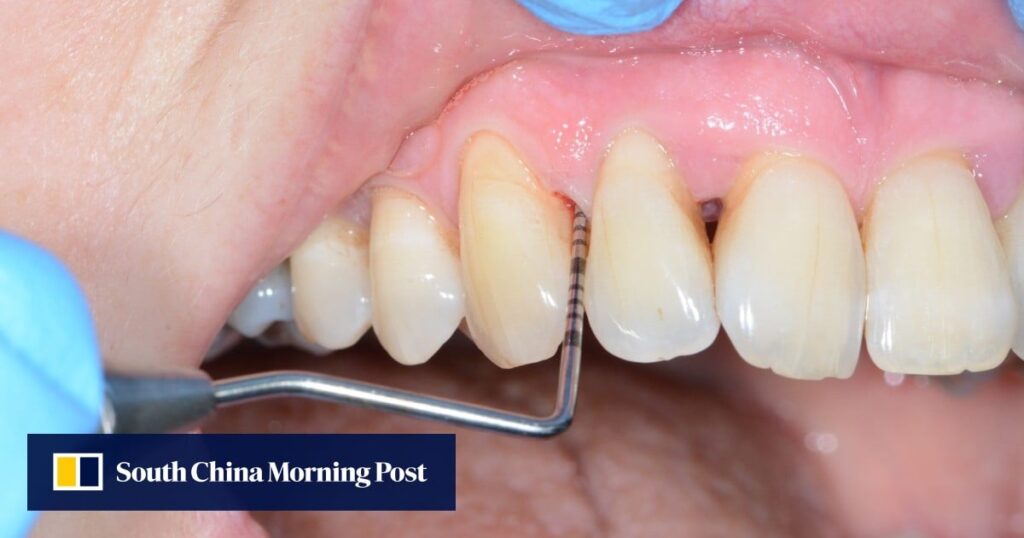
Our body's defense system normally suppresses these. But if you don't brush and floss regularly or neglect your oral health, plaque and tartar can build up and become a breeding ground for bad bacteria, which can lead to periodontal disease, Lee said. say.

There are two types. One is gingivitis, which only affects the soft gums and is reversible, and the other is periodontitis (symptoms include bad breath, loose teeth, and painful chewing) and is not reversible. This is an advanced form of periodontal disease that can't be cured, that is, damage. The effects on the bone and gum tissue are permanent and lead to tooth loss. ”
Part of what explains the close connection between oral health and systemic health is the body's immune system, which responds to injury and disease through inflammation, he explains.
“Inflammation can help the body heal, but if it continues, it can become chronic and lead to more serious problems, including periodontal disease, diabetes, heart disease, and respiratory infections.” and All dementias are diseases associated with inflammatory responses. ”
What is inflammation? Causes, symptoms, and treatments for chronic diseases
What is inflammation? Causes, symptoms, and treatments for chronic diseases
What happens is that even if the patient is not aware of the infection, disease-causing bacteria (pathogens) accumulate in the infected gums, spread through the blood vessels, and cause inflammation in the bloodstream. Possibly, West explains. Body tissues, including the brain, are located in close proximity to teeth and gums, and “there's a direct route to them,” West says.
According to one study, tooth loss is associated with an additional year of aging in the brain, and severe periodontal disease is associated with an additional 1.3 years of aging in the brain.

The exact relationship between poor dental health and reduced brain volume is unclear, but a Finnish study showed that people with poor dental hygiene were 21 percent more likely to develop Alzheimer's disease. Yes, says Lee.
Other studies have identified a bacterium called . Porphyromonas gingivalis This is related to periodontal disease. It and the enzyme it produces (gingipains) exist as strong risk factors for Alzheimer's disease. Both can cross the blood-brain barrier, “and both have been found in the brain tissue of people suffering from Alzheimer's disease,” Lee says.
Researchers at the University of Central Lancashire's School of Dentistry in the UK found that when the gingipain enzyme interacts with nerve cells in the brain, it “releases proteins that cause the cells to self-destruct and lead to cell death.”
“When a nerve cell dies, its proteins attach to neighboring healthy nerve cells, and the process repeats, potentially causing further damage to the brain as the disease spreads.”
“I'll put up with toothache”: Hong Kong's shortage of dentists creates poverty without receiving treatment
“I'll put up with toothache”: Hong Kong's shortage of dentists creates poverty without receiving treatment
Alzheimer's disease is associated with the accumulation of amyloid beta protein in the brain. Lee said the researchers identified an abundance of amyloid beta protein around the surface of infected teeth and diseased gums.
“Suggestions are that these proteins can travel through the bloodstream to the brain, increasing the risk of cognitive decline.”
West and Lee agree that it is inaccurate to suggest that all people with poor oral health will develop Alzheimer's disease.

“We know that if you have severe periodontitis, you are more likely to develop Alzheimer's disease,” says Lee.
At the same time, Dr. West says, “decreased cognitive abilities may lead to further deterioration in dental hygiene and health.”
I remember brushing her teeth becoming increasingly difficult as my mother's cognitive abilities began to decline. She said her mother couldn't remember how to brush her teeth or why she needed to do it.
Current research at the University of Bristol is investigating whether regular dental treatment for people with both Alzheimer's disease and periodontal disease may reduce cognitive decline or even cause an improvement in the condition. says West.
My mother's tooth loss may have been emblematic of her generation, who grew up without understanding or having access to the better oral care and electric toothbrushes we now have. However, it may also have been impaired by years of antidepressant medication.
Why you need good teeth and how to get a million dollar smile
Why you need good teeth and how to get a million dollar smile
Other drugs, aging, and health problems can all cause this problem. Lee says it's important to have enough saliva because it plays an important role in balancing the acids in your mouth and removing food particles and bacteria.
Lee said a significant number of elderly people in Hong Kong suffer from tooth decay and periodontal disease. A 2011 oral health survey found that “nearly half of non-institutionalized seniors aged 65 to 74 have untreated cavities, and nearly 90% have bleeding gums or signs of periodontal disease.” It turned out that he was having a problem.

So how can you care for your teeth now and in later life? West and Lee consistently advocate using a brush and floss or a small interdental brush after brushing.
“Follow a regular routine of brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing daily,” says Lee.
West says to use toothpaste with fluoride, and emphasizes that brushing your teeth before bed is especially important.
If your teeth are crooked or uneven, talk to your orthodontist to see if braces are right for you. Straight teeth are easier to clean and floss, which is important for maintaining good oral hygiene, Lee says.
Delving into the roots of ancient Chinese dentistry
Delving into the roots of ancient Chinese dentistry
There is no age limit for orthodontic treatment, but the sooner you receive it, the better.
Visit your dentist regularly for regular checkups and proper cleanings. Eat less sugar and sweet foods. Drink enough to reduce the effects of dry mouth and ask your dentist about artificial saliva sprays if you are taking medications that cause dry mouth.
And don't forget, just looking inside your mouth can give you great insight into your overall health.